7 Ways Hackers Steal Your Data Without Your Password

1. Phishing
Hackers send fake emails or texts that look like they’re from real companies. They create replicas of banking sites or social media logins to trick you into entering your credentials.
In 2014, a campaign targeted Gmail users with a success rate of 45%. To protect yourself, check email sender addresses, hover over links before clicking, and verify requests through official channels. If unsure, type the website URL directly instead of clicking links.
© Image Credit: Unsplash - Stephen Phillips
2. Keyloggers
Keyloggers record everything you type, including passwords, credit card numbers, and messages. They can be installed through downloads or email attachments. Kaspersky reported millions of malware instances annually (e.g., 560,000 new malware daily per Webroot), including keyloggers.
Use two-factor authentication because it adds a step keyloggers can't capture. Consider using password managers that auto-fill credentials, avoiding keyboard input entirely.

© Image Credit: Unsplash- Glenn Carstens-Peters
3. Public WiFi Interception
When you use public WiFi in places like cafes or airports, hackers on the same network can intercept data traffic. They might see websites you visit and capture login info if the connection isn’t encrypted.
About 20-30% of public WiFi networks lack proper security. Always use a VPN on public networks—it encrypts your traffic, keeping it safe. Avoid accessing sensitive accounts like banking or email on public WiFi unless necessary.

© Image Credit: Unsplash - Dreamlike Street
4. Session Hijacking
After you log into a website, your session is maintained through cookies or tokens. Hackers can steal these tokens to impersonate you without needing your password.
This often occurs on sites lacking proper security or when using unencrypted connections. Log out of important accounts when done, especially on shared computers. Enable automatic session timeouts where possible, and regularly check your account's active sessions to detect unauthorized access.
See also - The 13 Best Search Engines to Access the Invisible Web (The Deep Web)

© Image Credit: Unsplash - Artiom Vallat
5. SIM Swapping
Hackers may call your mobile carrier, pretend to be you, and convince them to transfer your phone number to a new SIM card. They can then receive your calls, texts, and password reset codes.
The FBI reported a 400% increase in SIM swapping complaints between 2018 and 2021. Use authentication apps instead of SMS for two-factor authentication when possible. Add a PIN or password to your mobile account to prevent unauthorized changes, and consider using a separate email for account recovery that's not tied to your phone.
If you enjoyed this guide, follow us for more.

© Image Credit: Unsplash - Andrey Metelev
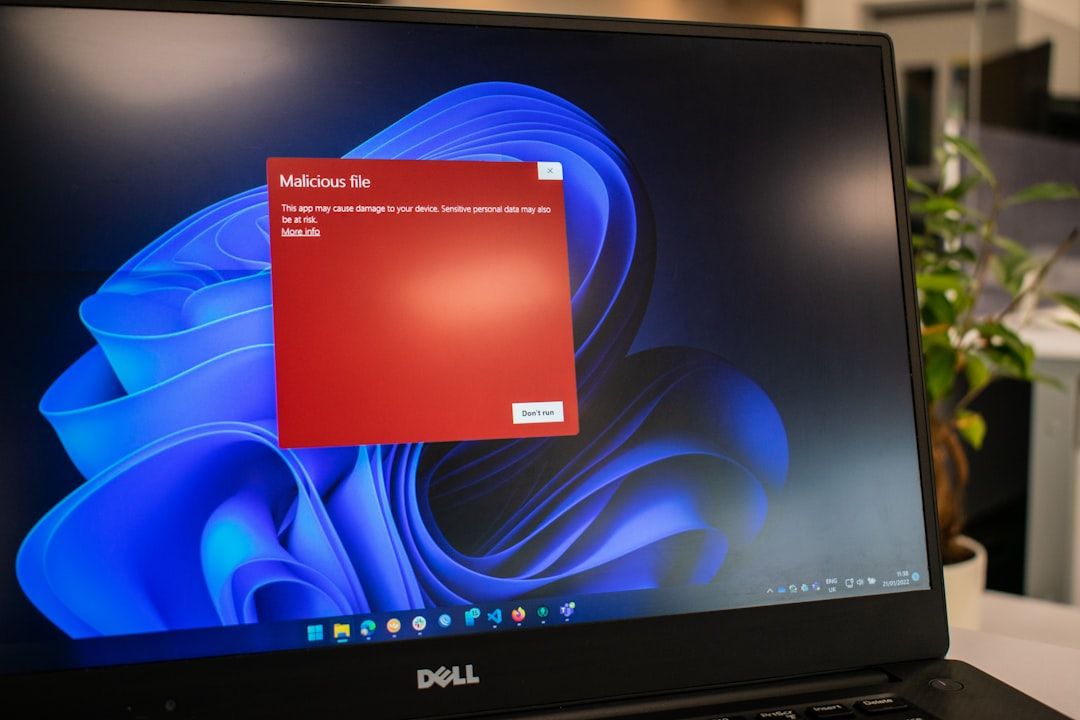
6. Malware
Malware can extract data from your device's memory, capture screenshots, or access your files without passwords. It often enters through downloads, infected USB drives, or compromised websites. About 560,000 new malware pieces are detected daily.
Keep your operating system and applications updated with the latest security patches. Use reputable antivirus software and run regular scans. Be cautious of downloading files from unknown sources, even if they look harmless.
© Image Credit: Unsplash - Ed Hardie
7. Social Engineering
Hackers gather information from social media and public records to trick people into revealing sensitive data. They might pretend to be tech support or a coworker. About 74% of cyberattacks involve social engineering.
Limit what personal information you share online, especially details that could be used in security questions. Be cautious with unsolicited contacts seeking information or access, even if they know personal details. Verify unusual requests through official channels before giving any information.
If you enjoyed this guide, follow us for more.

© Image Credit: Unsplash - Austin Distel
Recent
Highlights

If Your Fridge Has These 7 Smart Features, You're Paying Too Much
7 Ways Hackers Steal Your Data Without Your Password

Never Ignore These Privacy Alerts on Your TV (They're Not a Glitch)
15 Things You Didn't Know Your iPhone Could Do

12 Phone Settings That Are Secretly Exposing You to Hackers
