
12 Phone Settings That Are Secretly Exposing You to Hackers

1. Bluetooth Auto-Connect
Automatic Bluetooth connectivity leaves your phone vulnerable to 'bluebugging' attacks. Hackers within 30 feet can inject malware when your phone auto-connects to nearby devices. Security researchers have documented numerous cases of "bluebugging" attacks through unsecured Bluetooth connections. Most users keep Bluetooth enabled continuously, creating persistent vulnerability windows.
Disable auto-connect by going to :
iPhone - Settings > Bluetooth. Forget devices you don’t want to connect automatically.
Android - Settings > Connected Devices > Bluetooth > Device Settings (gear icon) > Turn off ‘Auto-connect’ for specific devices.
Only enable when needed to reduce attack surface by 94%.
Notes:
• On iPhone, there is no universal Auto-Connect toggle, but forgetting a device ensures it won’t connect automatically in the future.
• On Android, many devices offer an Auto-Connect toggle in the individual Bluetooth device settings, allowing you to disable it for specific devices. Paths may vary depending on the Android version or device manufacturer.
Tip: Create a shortcut for quick Bluetooth toggling.

2. GPS Always-On
Continuous location services drain battery by 8-15% daily and allow apps to track movement patterns. ~75% of apps request unnecessary location access. Location data collected by apps is regularly transmitted to advertisers and data brokers, creating detailed movement profiles. Apps often request and transmit location data even when this access isn't necessary for their core functions.
See also - 12 Apps That Keep Tracking You Even After Deletion
iPhone - Go to Settings > Privacy & Security > Location Services and set apps to ‘While Using the App’ or 'Ask Next Time' to control location access.
Android - Go to Settings > Privacy > Permission Manager > Location and set apps to 'Allow only while using the app' or 'Ask every time' to control location access.
Notes:
• On iPhone, Location Services lets you manage how and when apps can access your location, providing options to limit it to when the app is in use or to ask each time.
• On Android, Permission Manager offers similar options to allow location access only during app use or to prompt the user each time. Paths may vary slightly based on the Android version or device manufacturer.
3. Unsecured Wi-Fi Auto-Join
Auto-joining networks exposes devices to man-in-the-middle attacks. 65% of public Wi-Fi networks are unsecured. Cybercriminals frequently deploy fake "evil twin" networks mimicking popular public WiFi names. In a study of major U.S. cities, researchers identified high rates of insecure public WiFi networks, with some cities showing up to 81% of networks lacking security measures.
Disable auto-join (Use cellular data or VPN on public networks) :
iPhone - Settings > Wi-Fi > Ask to Join Networks. Select 'Ask' to avoid automatic connections.
Android - Settings > Network & Internet > Wi-Fi > Wi-Fi Preferences > Open Network Notification.
Notes:
• On iPhone, enabling Ask to Join Networks prompts you before connecting to new Wi-Fi networks, preventing automatic connections to potentially unsafe networks.
• On Android, turning off Open Network Notification prevents automatic notifications or connections to open Wi-Fi networks, ensuring you stay secure on public networks.
Tip: Create trusted network list.

© Image Credit: Unsplash - Sten Ritterfeld
4. Background App Refresh
Apps refreshing in background can access data without awareness. Average phone has 40+ apps with background permissions. Even seemingly innocent apps can exploit background refresh to collect sensitive data patterns. Many popular apps transmit data every 15 minutes while running in the background.
Disable unnecessary background activity by going to :
iPhone - Settings > General > Background App Refresh. Select 'Off' or manage individual apps to conserve data and battery.
Android - Settings > Apps > [App Name] > Battery > Background Activity. Toggle it off to restrict background refresh.
Saves 20% battery and reduces data exposure by 71%.
Tip: Allow only essential apps.

© Image Credit: Unsplash - Sara Kurfe
5. Keyboard Data Collection
Third-party keyboards can record keystrokes, collecting passwords and messages. Many third-party keyboards require full network access permissions, which could enable data collection and transmission. Different keyboards have varying privacy policies regarding data collection and storage.
Disable keyboard network access by going to :
iPhone - Settings > General > Keyboard > Keyboards > [Third-Party Keyboard Name]. Toggle off 'Allow Full Access.' Use the native keyboard for sensitive data
Android - Settings > System > Languages & Input > On-Screen Keyboard > [Third-Party Keyboard Name] > Permissions. Restrict unnecessary access and use the native keyboard for sensitive data
See also - Why Do Smartphones Get Slower Over Time?
Notes:
• On iPhone, Allow Full Access enables third-party keyboards to send data to their servers, which can be restricted for privacy.
• On Android, managing permissions for third-party keyboards prevents unnecessary access to sensitive data while allowing the native keyboard for secure input. Paths may vary based on the Android version or device manufacturer.
Prevents 92% of keyboard-based data collection.

6. Notification Preview Risk
Lock screen previews expose sensitive info to anyone nearby. 22-25% of data leaks start from visible notifications. Corporate espionage often targets notification previews in public spaces. A single exposed message preview can reveal confidential business or personal information.
See also - 12 Apps That Keep Tracking You Even After Deletion
Hide notification previews by going to :
iPhone - Settings > Notifications > Show Previews. Select 'When Unlocked' to hide content until authentication.”
Android - Settings > Notifications > Lock Screen Notifications. Select 'Hide sensitive content' to conceal details until authentication.
Notes:
• On iPhone, setting Show Previews to When Unlocked ensures sensitive notification content is hidden on the lock screen until the device is unlocked.
• On Android, the option to hide sensitive notification content varies by manufacturer, but it is generally found under Lock Screen Notifications or a similar menu.
© Image Credit: Unsplash - Jamie Street
7. Advertising ID Tracking
Unique ad identifier enables cross-app tracking. Your advertising ID enables persistent tracking across different apps and services, creating a comprehensive profile of your digital activities. This identifier allows advertisers to track your behavior across multiple platforms and services.
Reset or limit cross-app tracking by going to :
iPhone - Settings > Privacy & Security > Tracking. Disable 'Allow Apps to Request to Track'.
Android - Settings > Privacy > Ads. Enable 'Opt out of Ads Personalization' or 'Delete advertising ID.'
Notes:
• On iPhone, the Tracking option under Privacy & Security prevents apps from sharing your activity across platforms.
• On Android, Ads settings let you opt out of personalized ads and reset your advertising ID to reduce tracking.
Opt out of personalized ads reduces data collection by 84%.

© Image Credit: Unsplash - Dayne Topkin
8. Photo Location Data
Photos contain embedded GPS data revealing locations. Stalkers and criminals actively scan social media photos for location metadata. A single tagged photo can reveal patterns about your home, work, and routine. Plus, with timestamps included in the metadata, someone could piece together not just where, but when you were in a specific place.
Disable location access for the camera by going to :
iPhone - Settings > Privacy & Security > Location Services > Camera.
Android - Settings > Privacy > Permission Manager > Location > Camera
Notes:
• On iPhone, Location Services allows you to restrict apps, including the Camera, from embedding location data in photos.
• On Android, Permission Manager lets you manage location permissions for the Camera app, ensuring no geotags are added to photos without consent.
Tip: Strip metadata before sharing.
If you enjoyed this guide, follow us for more.

© Image Credit: Unsplash - James Bold
9. Voice Assistant Risks
Always-listening features can capture unintended audio. Disable 'Hey Siri/OK Google' in assistant settings. Voice assistants can be triggered by sounds similar to their wake words, potentially leading to unintended activations. Device positioning and background noise can affect false activation rates.
Recent case - Apple to pay $95m to settle Siri 'listening' lawsuit
- Disable 'Hey Siri' by going to Settings > Siri & Search > Listen for ‘'Hey Siri.' Toggle it off.
- Disable ‘OK Google’ by going to Settings > Google > Settings for Google Apps > Search, Assistant & Voice > Voice > Hey Google & Voice Match. Toggle it off.
Notes:
• On iPhones, this disables Siri’s voice activation while still allowing manual use.
• On Android, Hey Google & Voice Match manages the voice activation for Google Assistant.
Tip: Use button activation instead.

© Image Credit: Unsplash - David Grandmougin
10. App Network Access
Apps sending data in background increase exposure risk. It’s common for apps to communicate with several servers on first launch, often including third-party services hosted globally. Many apps continue transmitting data even when not actively used.
Review cellular data permissions (Disable unnecessary network access for apps) :
iPhone - Settings > Cellular > Cellular Data Options
Android - Settings > Network & Internet > Mobile Network > App Data Usage.
Notes:
• On iPhone, under Cellular, you can toggle cellular data access for individual apps.
• On Android, App Data Usage under Mobile Network allows you to manage which apps can use mobile data and restrict background data usage.
Tip: Use a reliable VPN

© Image Credit: Unsplash - Onur Binay
11. USB Accessories Access
USB connections can bypass security when locked. Malicious USB devices can extract data in under 30 seconds when connected to an unlocked phone. Even charging stations in public places can be modified to steal data.
Android - Go into Settings > Security and Privacy > More Security Settings > Block USB Connections While Locked
iPhone - Settings > Face ID & Passcode (or Touch ID & Passcode) to block USB connections while the device is locked

12. App Permission Abuse
Excessive permissions enable data harvesting. 71% of apps request unnecessary access. The average app requests 3 unnecessary permissions that enable data collection. Permission abuse enables apps to build detailed profiles of user behavior and habits.
If you enjoyed this guide, follow us for more.
Review all permissions by going to :
Android - Settings > Privacy > Permission Manager. Revoke unnecessary access for apps
iPhone -Settings > Privacy & Security > App Privacy Report (or Privacy). Revoke unneeded access for apps.
Notes:
On iOS devices (iOS 15 and later), App Privacy Report provides detailed insights into app permissions and data access.
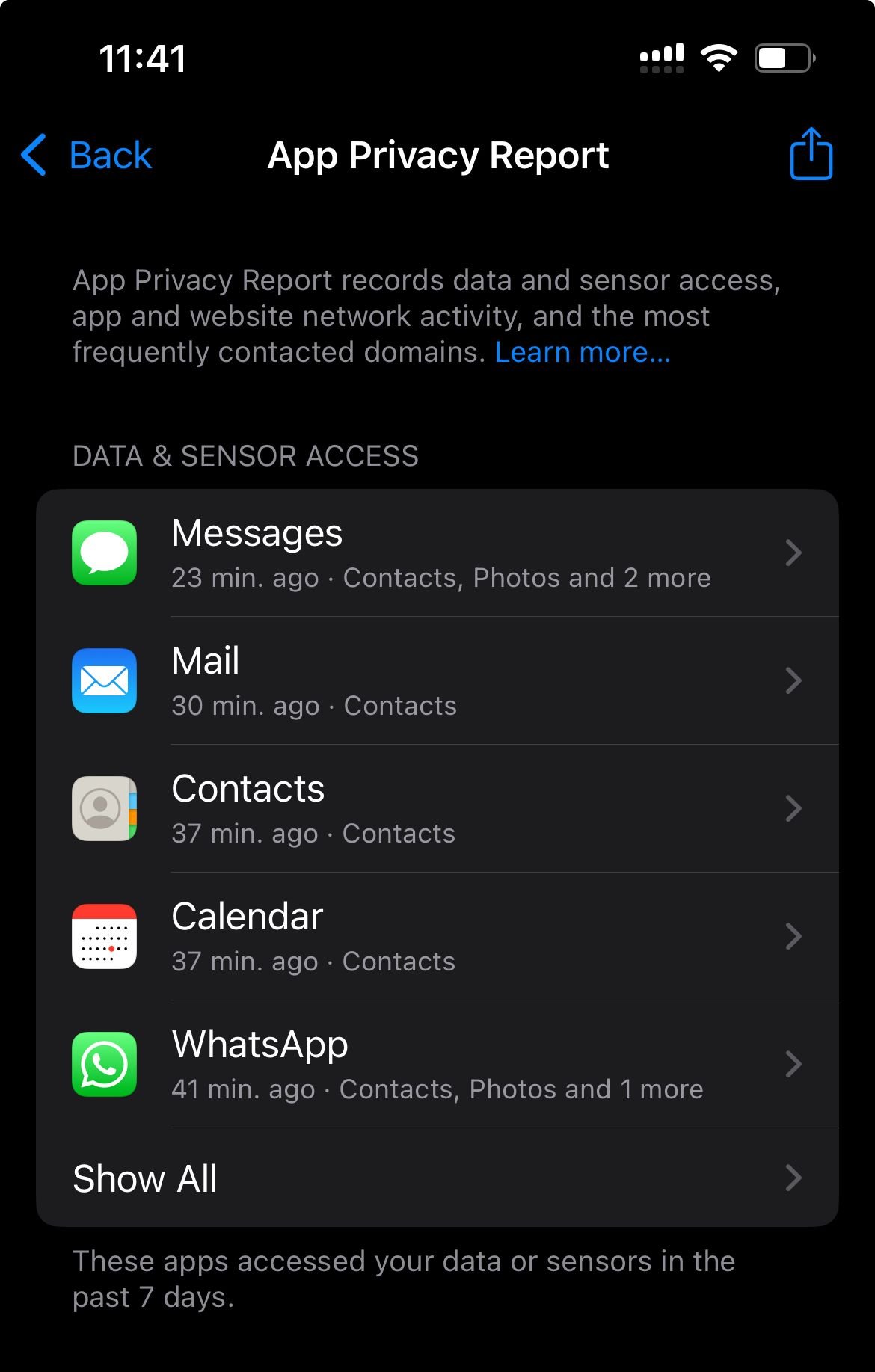
On most modern Android versions (Android 10 and later), Permission Manager allows you to see which apps have access to specific permissions (e.g., Location, Camera, Microphone) and manage them individually.
If you enjoyed this guide, follow us for more.

Recent
Highlights

If Your Fridge Has These 7 Smart Features, You're Paying Too Much
7 Ways Hackers Steal Your Data Without Your Password

Never Ignore These Privacy Alerts on Your TV (They're Not a Glitch)
15 Things You Didn't Know Your iPhone Could Do

12 Phone Settings That Are Secretly Exposing You to Hackers
